The first law of motion states that an object at rest tends to stays at rest. The object will remain at rest until an unbalanced force acts upon that object. If the object is in motion, it will continue to stay in motion in a straight line. An example for this law is when a person kicks a soccer ball. The ball is on the ground and is not in motion, but when someone kicks the ball, the ball is in motion and will continue to be in motion until another force(s) acts upon the ball, in this case air resistance and gravity.

Now that we've covered Newton's First law, lets talk about the second law. Newton's second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object is dependent upon two variables, the acceleration of the object and the mass of the object or F=MA. F stands for force, M stands for mass, and A stands for acceleration. This formula will allow you to calculate how much force it would take to move an object by multiplying the mass of an object by the acceleration of the object.
F=MA
Finally, Newton's third law of motion states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. The statement means that in every interaction, a pair of forces is acting on the two interacting objects. This law is why birds can fly and how we got people to the moon. Another example is fish swimming in water. A fish uses its fins to push water backwards. But a push on the water will only serve to accelerate the water. Since forces result from mutual interactions, the water must also be pushing the fish forwards, propelling the fish through the water.
Thanks for reading this post, and please leave a comment in the comment section down below.

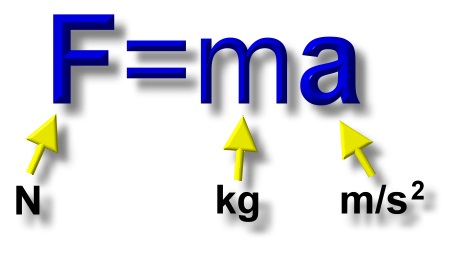
No comments:
Post a Comment